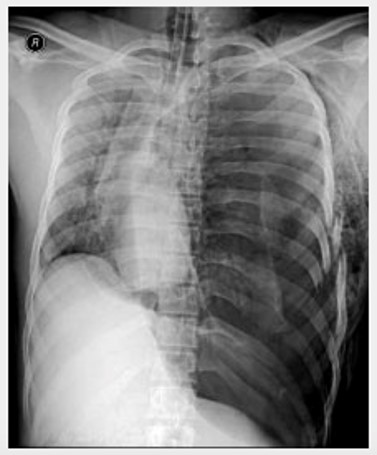
•Air enters the pleural space, but cannot escape
•Pressure in the pleural cavity collapses the ipsilateral lung
•Mediastinum shifts to the opposite side, compressing the contralateral lung
•Mediastinum shift impairs venous return to the heart, thereby reducing cardiac output
•Simple pneumothorax can become tension pneumothorax when positive pressure ventilation applied